Beyond the Racket: Intellectual Property in the World of Badminton
The 2022 Asian Games ended yesterday with a victory for the People’s Republic of China (PRC) with 383 medals. This achievement is far beyond Japan and South Korea, who are in second and third place with 188 and 190 medals. It is called the 2022 Asian Games because this 4 (four) annual event was supposed to be held in 2022, but due to the COVID-19 pandemic, it was finally shifted to September-October 2023, still in Hangzhou, China.
Of the 40 sports that are contested, 481 competitions have their charm. Imagine the enormous potential for sponsors when billions of eyes from different countries are focused on their favorite matches. Local brands can be instantly recognized throughout Asia.
The Trademark is not only displayed on the sidelines but also on the team shirts of each country. Therefore, the team’s failure to compete until the end is also a loss for their sponsors.
At the 2022 Asian Games, the Indonesian Badminton Team failed to win a medal for the first time since competing in 1962. So, what kind of Intellectual Property is there in Badminton?
1. Copyrights
Copyright Law applies to various aspects of Badminton, including written materials like coaching manuals, training guides, and literature related to the sport. Photographs and videos of Badminton matches, tournaments, and events are protected by Copyright. The rights to reproduce, distribute, and display these materials are typically owned by the creators, organizations, or governing bodies involved in Badminton.
Source: Asian Games 2022 Organising Committee’s Official Website
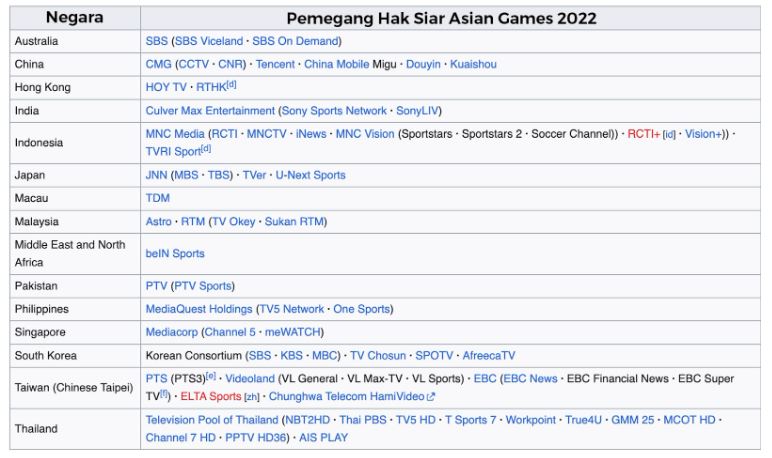
Copyrights also apply to broadcasting and live streaming of Badminton matches and events. Broadcasting companies and event organizers have exclusive rights to transmit these events, and unauthorized use can lead to Copyright Infringement claims.
2. Trademarks
Trademarks protect logos, brand names, symbols, and mascots associated with Badminton equipment manufacturers, event organizers, and governing bodies. For example, recognizable Trademarks like the Yonex logo are protected to prevent unauthorized use that could confuse consumers or dilute the brand’s reputation.

Source: Asian Games 2022 Organising Committee’s Official Website
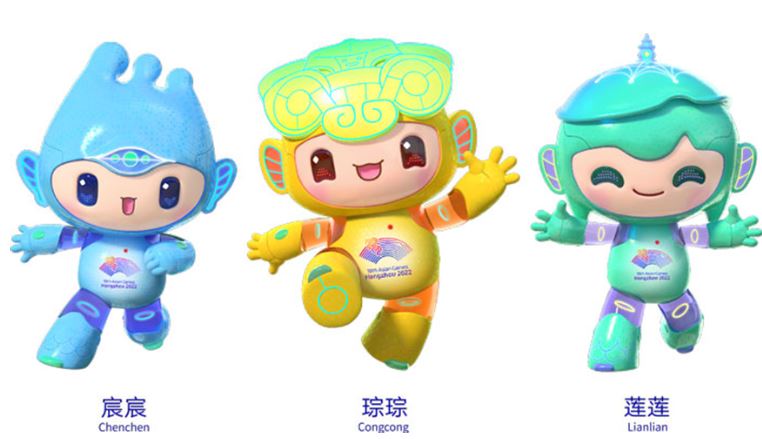
When discussing a big event like the Asian Games, mascots and merchandise cannot be missed because many participants and spectators will hunt for merchandise as souvenirs. For this reason, the organizer needs to register the event name in various Trademark classes that protect merchandise products.
3. Patents
Patents come into play when Badminton equipment or technological innovations are developed. This could include Patent protection for new racket designs, shuttlecock technologies, or other equipment that offers a unique and inventive solution. These Patents prevent others from making, selling, or using these innovations without permission.

Source: United States Patent Office
4. Trade Secrets
Some aspects of Badminton, especially proprietary techniques or training methods used by elite athletes or coaches, may be considered Trade Secrets. These are typically not publicly disclosed and are protected by maintaining their confidentiality. Unauthorized access or disclosure can lead to legal action.
It’s important to note that the specific IP regimes and their enforcement can vary from country to country and depend on the agreements between stakeholders in Badminton, such as equipment manufacturers, athletes, event organizers, and governing bodies. Legal protections are in place to encourage innovation, protect commercial interests, and ensure that the sport is conducted fairly and with respect for the Intellectual Property of all involved parties.
If you need further information about Trademark registration, Patent protection, or anything related to Intellectual Property, please do not hesitate to contact us via [email protected].