Summary of Implementation Guideline and Technical Guideline of Patent Substantive Examination in Indonesia
TECHNICAL GUIDELINE
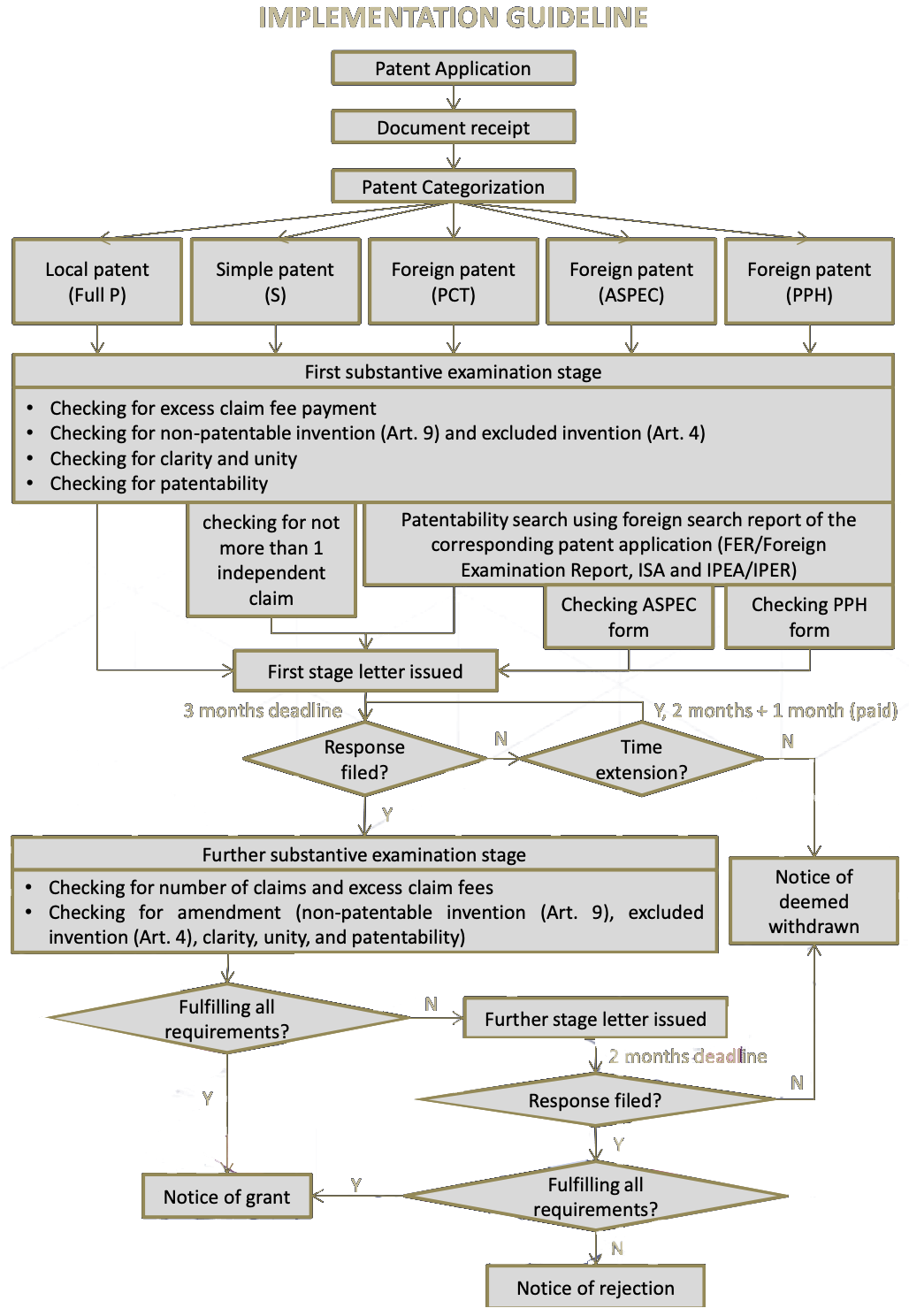
Patent Substantive Examinations are conducted within 30 months from the application date and will focus on the following points:
DESCRIPTION
- At Least Should Consist of:
a. Description regarding one way to conduct the invention;
b. If the description refers to figure, it should use the same reference as used in figures;
c. Description on how the invention is implemented in industry;
d. Brief description of invention for understanding regarding the invention;
e. Mention of technology in closest prior art in the background of invention.
- Includes in the Following Order:
-
- Technical Field of Invention;
- Background of Invention;
- Brief Description of Invention;
- Brief Description of Drawings (if available);
- Detailed Description of Invention.
- Sufficiency of Disclosure
-
- Description should disclose the invention clearly, such that those skilled in the art can implement the said invention. This is so that the public can utilize this invention in return for the right granted to the applicant.
- The function of the invention should be disclosed.
- Prior Art Background
-
- Inventor should state what is considered as the closest prior art in the background of the invention. If the search result finds a closer prior art, the closest prior art should be mentioned in the background of the invention.
- In mentioning the prior art the background should be fair and honest and should not be misleading.
CLAIMS
- Product Claims vs Process Claims
There are only 2 categories of claim:
-
- Product Claims:
For a physical entity (object). Products may be a compound, an equipment, a combination of equipment in a system, etc. Product claim cannot be distinguished from prior arts through its method of use. - Process Claims:
For an activity (method). Processes may be an activity to produce a product, an activity which use a product, or an activity which use an organism as a subject.
- Product Claims:
- Independent vs Dependent Claims
-
- Independent Claim consists of all features of the invention which protection is sought . Independent claim does not depend in content on another claim.
- Dependent Claim consists of all features from independent and/or other dependent claim and has the same category as the claim which it depends on.
Dependent Claim cannot:
-
-
- belong to a different claim category than the claim it depends on;
- be broader than the claim which it depends on;
- contain other features which are not in the claim it depends on;
- refer to a subject matter from another claim for intended purpose; and
- only refer to a part of the claim which it depends on.
-
Dependent Claim can depend on more than 1 claim.
If a dependent claim disclose a feature which were not described previously, the independent claim should describe this feature, or the dependent claim must first describe this feature.
- Product by Process Claims
Product by process claim is not novel just because it is produced by a novel process. Its novelty and inventive step are determined through its own product features.
- Feature
Product claim should contain product features, process claim should contain process features.
- Alternative in Claims
Claim may refer to alternative forms ”and/or”, but each alternative should have the same basic properties. One alternative must be able to replace another.
- Two Parts Form Claim (Preferable Form)
-
- First Part:
Preamble consisting of technical features of said invention that is known from previous technology. - Second Part:
Technical features of invention which distinguish the invention from the previous technology and which protection is sought.
- First Part:
For simple patent, all (tangible) product claim and the dependent claim thereof should be written in two parts form.
- Figures and Graphs and References in Claims
-
- Claims cannot contain figures or graphs, but may contain tables and mathematical formulas.
- For clarity, notation which refers to figures may be added and should be written uniformly between brackets ( ).
- Parameters in Claims
Parameters are values which are properties of a product that can be measured directly. Characterization of product using only parameters are not allowed unless the invention is unable to be described using other means. Method of measurement:
-
- Too long to be described in the claim;
- Those skilled in the art know which method to use, because there is only one method commonly used;
- All measurement methods yield in the same result.
- Consistency
-
- Writing of claims should be consistent between one feature to another, e.g.. using present or past participle, using active or passive voice.
- Claims should be consistent with the description. The description should contain the same limiting features as the claims.
- If the description states that one feature is essential for the invention, said feature must be included in the independent claim.
- If some embodiments in the description are not included in the claims, the claims may be broaden to include these embodiments or these embodiment may be deleted from the description.
- All terms used in claims should be consistent with the description, all uncommon terms should be defined in the description.
AMENDMENT
Amendment cannot broaden the scope of the invention (by adding a subject matter), but may be allowed if it is intended to clarify the disclosure.
UNITY
Invention should have the same common inventive concept. Unity of invention can be considered for the following combination of independent claims:
a. Product claim, process claim which is specifically used for the manufacture of said product;
b. Process claim and equipment/apparatus claim which is specifically designed to conduct said process; and
c. Product claim, process claim which is specifically used to manufacture said product and equipment/apparatus claim which is specifically designed to conduct said manufacturing process of said product.
PRIORITY
Priority rights are granted for the following:
a. Paris convention or WTO member countries;
b. Applications claiming priority which is filed within 12 months since the filing date of the priority application;
c. Previous invention should have been filed by applicant of Indonesian application, or Indonesian applicant should be a rightful surrogate of the applicant of the previous application;
d. Application should be of the same invention as the previous invention;
e. Previous invention should be the first application for said invention;
f. The first application should have been filed on or to a country signing Paris convention or WTO.
CHEMISTRY
- Product by Process Claims
Product by process claims are product claims characterized by process features. Product by process claims are allowed if:
-
- Product cannot be described using parameters of product.
- Said product is novel.
- Product Characterized by Parameters
-
- In section 3.34, product claims should not be characterized by parameters.
- Parameters can be used to characterize a product when the product cannot be characterized using other means.
- In certain field such as nanotechnology, to determine the novelty of a product characterized by process, parameter values of the final product can be used as a limiting feature which determine novelty.
- Product Characterized by Function
-
- Function can be used as limiting feature which determine novelty and inventive step.
- Function is used as a limiting feature when the product cannot be characterized by other means.
- One example is claim regarding a catalyst which can only be described through its function in a process.
- Measurement of parameters
-
- If the claim disclose a parameter, the claim should specify clearly which method of measurement is used to obtain such parameter.
- For example a claim is considered unclear when it disclose MFR (mass flow rate) as a parameter, meanwhile ISO 1133:2005 specifies two procedures for measurement of MFR, I.e. mass measurement method and displacement measurement method.
BIOLOGY
- Microorganism
-
- Microorganisms are yeast, fungi, bacteria, and actinomycetes.
- Microorganism includes human cell and plant cell.
- Clarity: Should be characterized by the correct nomenclature, strain name should be written after the species name.
-
- Novelty: New strain should be described specifically and the difference with known strain from the same species should be described.
-
- New species: Characterized by taxonomy and phylogenetic tree
- Inventive step: A novel microorganism having different taxonomy is inventive.
- Non patentable are embryo, seeds, part of plants, tissue, organs, and transgenic plants.
- Non-Essential Biological Process
-
- Non-essential biological process are biological processes which need human intervention.
- Example: Plant tissue isolation method
- Non-patentable are artificial insemination, cross pollination, and other processes which can occur naturally without human intervention.
- Microbiological Process
-
- Microbiological process are biological processes which use microorganism.
- Example: Fermentation
- Nucleotides and Genetic Engineering
-
- Nucleotides are DNA, cDNA, primer, gene, vector, transforman.
- Patentable nucleotides are isolated nucleotides.
- Novelty: Examined with BLAST or NCBI.
- Inventive Step: if it has different activity at least qualitatively, it is considered inventive.
- Gene can be characterized by polynucleotide sequence, amino acid sequence encoded by said polynucleotide, or mutation.
- Vector can be characterized by DNA sequence, DNA restriction map, molecular weight, and number of base pair.
- Transforman can be characterized with 1 host cell and the introduced gene (sequence).
PHARMACY
- Pharmaceutical Invention may be in the form of:
-
- Physical entity: Product or device and composition or compound
- Activity: Process and method
- Non Limiting or Non Distinguishing Technical Feature:
-
- Dosing regimen
- Administration time or frequency
- Patient group
- New Use for known or existing product is patentable when:
-
- The protection of claims is directed to compound X with the feature of “disease Y” as a limiting or distinguishing feature.
- In this case, the claim protection is intended wherein a pharmaceutical industry may produce drug X which is indicated only to treat hypertension.
- Drug Mechanism of Action
-
- Features solely defined as mechanism of action is considered as too broad and not patentable.
- “Activity or Use” feature which can be used as limiting/distinguishing features are those intended to treat or prevent certain diseases wherein the efficacy is supported by clinical trial data described in the description.
- New Form
-
- New Form of a known compound is not considered an invention if it does not give any meaningful efficacy improvement and does not have any chemical structural difference in relation to what is known from the compound.
- Meaningful efficacy improvement includes improvement in bioavailability, stability, solubility, toxicity, potency, etc. Meaningful efficacy improvement should be supported by experimental data.
- Example of New Forms: chirality, crystal/solvate/hydrate, salt.
- Method of treatment
-
- In vitro, ex vivo, and in silico method of examination or diagnosis are patentable. In vivo method of examination or diagnosis is not patentable.
- Non-therapeutic method of treatment is patentable. Therapeutic method of treatment is not patentable.
- Method of surgery is not patentable.
- Method of medication applied directly to animal and/or human is not patentable.
- Natural medicine
-
- Product by process claims are allowed when it is difficult to define the product itself except by process features: Example: defining extract by its process of extraction.
- Each step in the process of making herbal product affect the quality, safety, and efficacy of the product.
- Process features in herbal product preparation can be used in determining the novelty and inventive step.
ELECTRO & PHYSICS
- Computer-Implemented Invention
Computer implemented invention is an invention which implementation use computer. One or more feature of the invention is fully or partly realized by a computer program. The feature of a computer implemented invention is a program feature. In this invention, source code should not be included in the description or claims. A computer program is considered as an invention if it has technical features:-
- It has a technical means, e.g. computer, server, phone, censors, devices.
- It produce, when run on a computer, a further technical feature outside of normal physical interaction between computer program (software) and computer.
-
Categories:
-
-
- Process Method Product
- System Device Product (computer program)
Computer-readable storage mediasoftware.
-
- Business Method
Computer-implemented business method is patentable as long as the subject matter has technical character.
- Artificial Intelligence
AI and ML are basically mathematical models which are implemented by software. The technical guideline has not said anything regarding AI and ML.